"don't automate your automation" :)
poniedziałek, 8 grudnia 2014
Understanding puppet part 1
First two youtube movies - and I know much more...
"don't automate your automation" :)
"don't automate your automation" :)
poniedziałek, 17 listopada 2014
RHCSE - firewall
Short reference to firewalld:
yum install iptables-services
systemctl start iptables
systemctl start ip6tables
systemctl enable iptables
systemctl enable ip6tables
systemctl enable firewalld
systemctl start firewalld
Zones list with description (https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/FirewallD#Dynamic_firewall_with_FirewallD)
drop - Any incoming network packets are dropped, there is no reply. Only outgoing network connections are possible.
block - Any incoming network connections are rejected with an icmp-host-prohibited message for IPv4 and icmp6-adm-prohibited for IPv6. Only network connections initiated within this system are possible.
public - For use in public areas. You do not trust the other computers on networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
external - For use on external networks with masquerading enabled especially for routers. You do not trust the other computers on networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
dmz - For computers in your demilitarized zone that are publicly-accessible with limited access to your internal network. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
work - For use in work areas. You mostly trust the other computers on networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
home - For use in home areas. You mostly trust the other computers on networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
internal - For use on internal networks. You mostly trust the other computers on the networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
trusted - All network connections are accepted.
firewall-cmd --get-services (to list all avaliable services)
firewall-cmd [--zone=] --add-interface=
firewall-cmd [--zone=] --change-interface=
firewall-cmd [--zone=] --remove-interface=
firewall-cmd [--zone=] --query-interface=
firewall-cmd --panic-ooff
firewall-cmd [--zone=] --add-service=
To delete --remove-service and to query --query-service
If there is no service and you have to open specified port just use:
--add-port --remove-port --query-port
Disable firewalld and install iptables service:
systemctl disable firewalldyum install iptables-services
systemctl start iptables
systemctl start ip6tables
systemctl enable iptables
systemctl enable ip6tables
Reverse - use firewalld instead of iptables:
systemctl disable iptablessystemctl enable firewalld
systemctl start firewalld
Working with firewall-cmd:
firewall-cmd --list-all-zones (to list all avaliable zones) or firewall-cms --get-zonesZones list with description (https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/FirewallD#Dynamic_firewall_with_FirewallD)
drop - Any incoming network packets are dropped, there is no reply. Only outgoing network connections are possible.
block - Any incoming network connections are rejected with an icmp-host-prohibited message for IPv4 and icmp6-adm-prohibited for IPv6. Only network connections initiated within this system are possible.
public - For use in public areas. You do not trust the other computers on networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
external - For use on external networks with masquerading enabled especially for routers. You do not trust the other computers on networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
dmz - For computers in your demilitarized zone that are publicly-accessible with limited access to your internal network. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
work - For use in work areas. You mostly trust the other computers on networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
home - For use in home areas. You mostly trust the other computers on networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
internal - For use on internal networks. You mostly trust the other computers on the networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
trusted - All network connections are accepted.
firewall-cmd --get-services (to list all avaliable services)
Managment of zone / interface:
firewall-cmd --get-zone-of-interface=p3p1 (get zone assigned to p3p1 interface - old eht0 in my environment)firewall-cmd [--zone=
firewall-cmd [--zone=
firewall-cmd [--zone=
firewall-cmd [--zone=
Panic mode:
firewall-cmd --panic-onfirewall-cmd --panic-ooff
Zone / service management:
If no zone is specified default zone is used (firewall-cmd --get-default-zone)firewall-cmd [--zone=
To delete --remove-service and to query --query-service
If there is no service and you have to open specified port just use:
--add-port --remove-port --query-port
For router:
firewall-cmd [--zone=] --add-masquerade / --remove-masquerade / --query-masquerade
All changes made by firewall-cmd work with no need of restart of firewall service, but are not pernament by default. If you need save them use --pernamet parameter of firewall-cmd.
How to make changes pernament:
All changes made by firewall-cmd work with no need of restart of firewall service, but are not pernament by default. If you need save them use --pernamet parameter of firewall-cmd.Configuration files:
Current configuration files of zonez are kept in: /etc/firewalld/zones, but default settings in /usr/lib/firewalldpiątek, 5 kwietnia 2013
Checking files with .sign keys
Question: how to verify file with .sign key (for example updates downloaded from dell sites)
- first you have to generate your own certificate with gpg: gpg --gen-key
- download public key (ex: http://lists.us.dell.com/linux-security-publickey.txt)
- import public key gpg --import linux-security-publickey.txt
- sign public key: gpg --edit-key linux-security@dell.com then fpr (for check fingerprint) and (sign for signature check)
- check file with gpg command:
gpg --verify PER210_BMC_FRMW_LX_R278576.BIN.sign PER210_BMC_FRMW_LX_R278576.BIN
Result in Polish:
gpg: Podpisano w pon, 16 sie 2010, 13:41:21 CEST kluczem DSA o numerze 23B66A9D
gpg: Poprawny podpis złożony przez ,,Dell, Inc. (Product Group) ''
niedziela, 20 listopada 2011
poniedziałek, 7 listopada 2011
Power consumption with Ubuntu on Samsung NP350U2A
For couple of weeks I have been searching for new laptop (replacement for my old ThinkPad T61).
As I remember on my old T minimum power consumption was something about 19W.
Now with new Intel Core i5 my Ubuntu can work with only 8W!

Powertop on normal work - screen backlight on 50%, WiFi on and Chromium browser running (in background apache, mysql and so on)
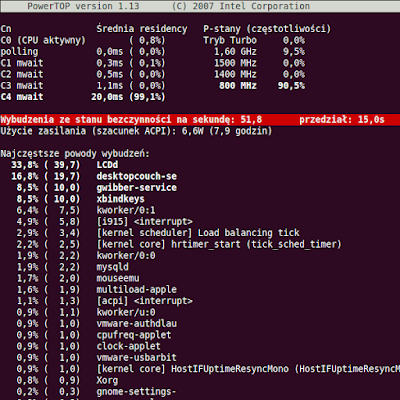
Powertop on minimum power usage (almost everything turned off, screen backlight to minimum)
As I remember on my old T minimum power consumption was something about 19W.
Now with new Intel Core i5 my Ubuntu can work with only 8W!

Powertop on normal work - screen backlight on 50%, WiFi on and Chromium browser running (in background apache, mysql and so on)

Powertop on minimum power usage (almost everything turned off, screen backlight to minimum)
/var/log/messages on ubuntu 11.4
Why they do that?? Writing log's to /var/log/messages should be enabled by default...
To often I use this file to figure out what is going on. But there is simple solution for that:
and uncomment lines in section caled
To often I use this file to figure out what is going on. But there is simple solution for that:
vim /etc/rsyslog.d/50-default.conf
and uncomment lines in section caled
# Some "catch-all" log files.
Subskrybuj:
Posty (Atom)
